Dating groundwater
Research Status: Past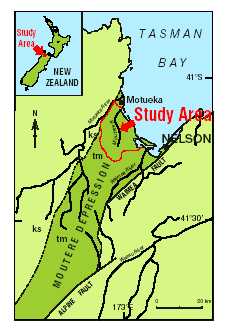 |
Moutere depression |
Introduction
Groundwater flow in aquifers occurs in response to hydraulic gradients between their recharge and discharge areas. Strong climatic fluctuations in the Quaternary caused repeated rise and fall of sea level, leading to drastic effects on groundwater flow in aquifers. In particular, the rapid rise of sea level (around 10,000 years BP) after the last glacial maximum at 18,000 years BP is likely to have trapped "paleo" waters at deeper levels in coastal aquifers. We have identified such paleowater in the deepest Moutere Gravel aquifer.
Research Approach
Radiocarbon, oxygen-18 and chemical concentrations have been used to investigate the history of groundwater in Moutere Gravel aquifers near Nelson.
Research Results
Scientists studying an aquifer in the Nelson-Motueka area have found what they believe is the oldest fresh water in New Zealand.
The Moutere aquifer contains high quality glacial-age water more than 20,000 years old, said groundwater scientist Mike Stewart of GNS (Geological and Nuclear Sciences Ltd).
The aquifer, which is 400m to 500m deep, contains a large body of water which probably extends offshore into Tasman Bay.
Recent Publications
Recent Presentations
| Year | Title | File Size |
| 2002 | How old is groundwater in the Upper Motueka catchment and what does age say about groundwater? | |
BMPs, BEPs and Guidelines
| Title | Description |
| A National Protocol for State of the Environment Groundwater Sampling in New Zealand |
From website: This document provides a step–by–step protocol for the collection of...More » |
Primary Contacts:

|
Mike Stewart
Email Phone: 04 570 4803 Fax: 04 570 4603 |
Institute GNS |
Expertise Groundwater studies, isotope tracing |