Thalweg Mapping: A measure of habitat quality
Research Status: Ongoing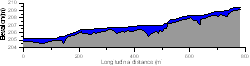 |
Thalweg profile of Motueka River at Norths Bridge |
Introduction
Experienced anglers know how important pools are for providing suitable habitat for adult trout - especially in smaller rivers where water depth in other parts of the river may be insufficient to support fish. A common message from anglers fishing the Motueka River, and other rivers affected by sediment, is “there used to be more pools than there are now and they were deeper”. This anecdotal information is highly relevant to trying to understand changes in fish populations, but unfortunately there is rarely any data available to support these claims. Most of the habitat measures that are commonly used around the world are highly subjective and measurements vary substantially among survey teams (e.g. cover, embeddedness). Other metrics are heavily dependent on river flow at the time when the survey is done. For example, a section of river that is classified as a run at one flow will become a riffle at a lower flow. One measure that is independent of river flow, and repeatable, is the occurrence and size of ‘residual’ pools. Imagine if a river stopped flowing, there would still be pools left behind. These are the residual pools - and their location, length and depth can be measured at any flow. Overseas studies have shown that the abundance of residual pools and the mean depth of those pools are closely related to fish abundance.
Research Approach
As part of a study attempting to model catchment-wide patterns of fish abundance and the effects of flow variability we have been measuring residual pool depths and abundance at sites throughout the Motueka Catchment. The measurements involve an accurate survey of the shape of the river bed along a reach. This process is called thalweg mapping and focuses only on the central, deepest part of the channel.
Research Results
Results collected so far indicate some major differences among different parts of the catchment. Some sections have many deep residual pools (e.g. Motupiko @ Korere) that will provide good habitat for fish, whereas other sections are relatively featureless and offer poor habitat (e.g. Motueka @ Norths Bridge). During 2007/08 we aim to cover a broader range of sites and relate these physical measures to assessments of fish abundance.
 |
 |
Motueka River |
Upper Motueka River |
Recent Publications
| Year | Title | File Size |
| 2012 | A Summary of Outcomes and selected formal publications from the Integrated Catchment Management (ICM)research programme:2000 – 2011 |
|
Primary Contacts:
1.jpg)
|
Joe Hay
Email Phone: 0064 3 5393277 |
Institute Cawthron Institute |
Expertise Habitat modelling, Freshwater fisheries |

|
Trevor James
Email |
Institute Tasman District Council |
Expertise Water Quality and Aquatic Ecology |

|
Roger Young
Email Phone: (03) 548 2319 Fax: (03) 546 9464 |
Institute Cawthron Institute |
Expertise Land/water interactions, water quality, fisheries, river health |